Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, combining Proxmox and QNAP can unlock powerful, flexible, and cost-efficient virtualization and storage solutions. Whether you’re a home lab enthusiast or a small business owner, this pairing can help you create a robust environment for virtual machines (VMs), backups, and network-attached storage (NAS).
What Is Proxmox and QNAP?
Proxmox and QNAP is an open-source platform that integrates two virtualization technologies, KVM for virtual machines and LXC for containers, into a powerful web-based interface. It’s commonly used to manage virtual environments efficiently and supports high availability, software-defined storage, and backups.
QNAP (Quality Network Appliance Provider) is a brand of NAS devices that provide centralized data storage, backup, file sharing, and media services. QNAP NAS systems run on their custom OS and are widely used in both home and enterprise environments for storage and application hosting. Some QNAP models may include or support components like the IDT70V261 for enhanced memory access or performance in specialized configurations.
What Is QNAP Used For?
QNAP NAS devices are primarily used for:
- Centralized file storage and sharing
- Backup solutions for PCs, servers, and virtual machines
- Multimedia streaming and media servers
- Surveillance with IP camera integration
- Virtualization Station for running VMs on the NAS
- Docker and container application hosting
What Can Proxmox Be Used For?
Proxmox is ideal for:
- Running multiple virtual machines and containers
- Creating high-availability clusters
- Managing backups and replication
- Testing different operating systems and services
- Hosting services for production or testing environments
- Efficient hardware resource management
Installing Proxmox on QNAP NAS
Installing Proxmox directly on a QNAP NAS is not natively supported, but you can run Proxmox as a virtual machine within QNAP’s Virtualization Station or use the NAS for storage in a separate Proxmox server setup. This allows you to leverage QNAP’s robust storage capabilities alongside Proxmox’s powerful virtualization features.
Virtualization Station
Virtualization Station is QNAP’s built-in hypervisor that allows you to run multiple virtual machines directly on compatible QNAP NAS devices. It supports various operating systems like Windows, Linux, and others, providing an easy-to-use web interface for VM management. This feature enables users to combine storage and virtualization in a single device without needing separate hardware.
QNAP Bootable USB or iSCSI
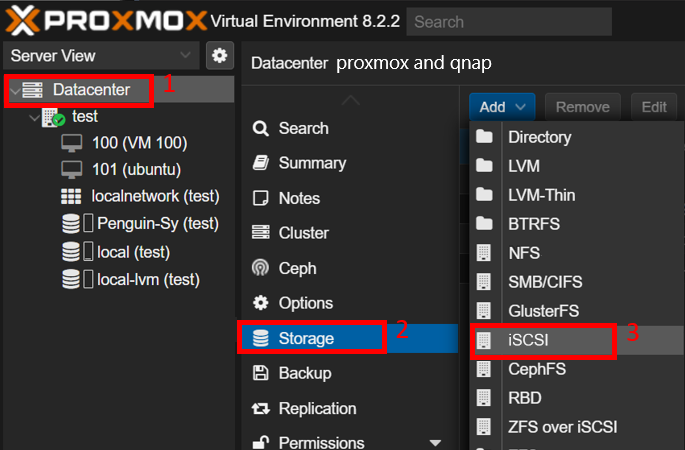
QNAP devices can use bootable USB drives to load alternative operating systems or tools like Proxmox, allowing flexible system setups without altering the NAS OS. iSCSI enables QNAP NAS to present storage as a block device over the network, which Proxmox can use as direct VM storage. Together, these methods enhance Proxmox and QNAP integration by expanding storage and boot options.
External Mini-PC or Server with QNAP as Storage
You can run Proxmox on an external mini-PC or dedicated server while using the QNAP NAS solely for storage via network protocols like NFS or iSCSI. This setup separates compute and storage, optimizing performance and flexibility. It allows Proxmox to handle virtualization tasks while leveraging QNAP’s reliable, centralized storage capabilities.
Why Use Proxmox for NAS?
While QNAP is a robust NAS solution, Proxmox adds:
- Virtualization capability beyond QNAP’s built-in VM tools
- More flexible VM/container management
- Advanced clustering and backup tools
- Customizable networking and firewall options
What Is the Difference Between QNAP and NAS?
A NAS (Network Attached Storage) is a general term for any device designed to provide centralized storage accessible over a network. It allows multiple users or devices to store, share, and manage files in a convenient and centralized way. NAS devices typically include basic file sharing, backup capabilities, and sometimes media streaming functions.
QNAP, on the other hand, is a specific manufacturer and brand that produces NAS devices with a strong focus on advanced features, performance, and expandability. QNAP NAS units run on their proprietary operating system (QTS or QuTS hero) and offer extensive application ecosystems, including virtualization support, container hosting, surveillance management, cloud sync, and multimedia services.
As legacy services like Skype die or become obsolete, platforms like QNAP continue to evolve, offering integrated communication, storage, and cloud solutions in one device—making them more future-ready than traditional standalone apps.
Configuring QNAP for Proxmox Backups
You can configure your QNAP NAS as a backup target for Proxmox by:
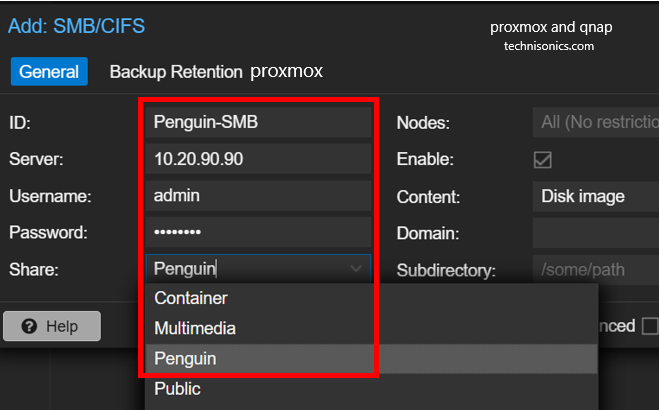
- Creating an NFS or CIFS/SMB Share on your QNAP.
- Mounting the Share in Proxmox via the GUI or /etc/pve/storage.cfg.
- Assigning it as a Backup Storage in Proxmox.
- Scheduling VM Backups to your QNAP share.
Can You Run a NAS on Proxmox?
Yes, you can run a NAS solution within Proxmox, such as:
- TrueNAS CORE or TrueNAS SCALE
- OpenMediaVault
- Nextcloud on Ubuntu/Debian
Proxmox Backup Server with QNAP Integration
You can deploy Proxmox Backup Server (PBS) and use QNAP as the backup storage target:
- Install PBS as a VM or on a separate host.
- Connect QNAP via NFS or SMB to the PBS.
- Configure datastore paths in the PBS interface.
- Integrate PBS with your main Proxmox VE for backups.
Which OS Does QNAP Use?
QNAP NAS devices run on proprietary operating systems designed to optimize storage performance and offer a wide range of features:
QTS
The standard OS for most QNAP NAS models, featuring an intuitive interface and powerful tools for file sharing, backups, multimedia streaming, virtualization, and app management.
QuTS hero
A ZFS-based OS designed for enterprise use, offering advanced data integrity, real-time deduplication, compression, and superior snapshot and backup capabilities.
QNE (QNAP Network OS)
Used in select QNAP appliances, QNE is tailored for networking-centric tasks and infrastructure deployment.
Best Practices for Proxmox & QNAP Setup
To ensure optimal performance, security, and reliability when integrating Proxmox and QNAP, follow these best practices:
Use NFS or iSCSI Protocols
Connect QNAP to Proxmox using NFS (for easier setup) or iSCSI (for better performance and block-level access), depending on your workload needs.
Separate Storage for Backups and VMs
Store virtual machines and backups on different volumes or shared folders to reduce I/O contention and improve performance.
Secure Network Shares
Set proper access controls, use strong passwords, and restrict IP access to ensure only Proxmox can access QNAP storage shares.
Monitor Disk Usage and Health
Regularly check QNAP storage usage and SMART status to prevent disk failure or over-provisioning that could disrupt your proxmox and qnap environment.
Keep Systems Updated
Always update Proxmox and QNAP firmware to the latest stable versions to benefit from performance improvements, security patches, and new features.
Use ZFS on Proxmox
When possible, use ZFS for your Proxmox storage layer. It works well with QNAP as backend storage and enables snapshots, replication, and data integrity features.
What Are the Cons of Proxmox?
While proxmox and qnap is a powerful and flexible virtualization platform, it does come with a few potential drawbacks to consider:
Steeper Learning Curve
Compared to consumer-grade NAS solutions like QNAP, Proxmox requires a deeper understanding of virtualization, networking, and storage concepts.
Limited Free Support
Official support is only available through a paid subscription. While community forums are active, enterprise users may find this limiting.
Technical Configuration Required
Setting up and maintaining a proxmox and qnap environment for production use demands more technical expertise, especially for clustering, backups, and high availability.
Smaller App Ecosystem
Unlike QNAP, proxmox and qnap doesn’t have a built-in app store or a wide range of third-party applications, focusing instead on core virtualization and containerization functions.
Benefits of Integrating Proxmox with QNAP NAS
Despite a few limitations, combining Proxmox and QNAP offers significant advantages for both home labs and professional environments:
Separation of Storage and Compute
Running proxmox and qnap on a dedicated server while using QNAP solely for storage ensures better resource allocation, scalability, and manageability.
Flexible Backup and Disaster Recovery
QNAP can serve as a reliable target for proxmox and qnap backups via NFS, SMB, or iSCSI, offering snapshot support, versioning, and offsite replication.
Cost-Effective Virtualization
Compared to commercial platforms like VMware or Microsoft Hyper-V, Proxmox provides enterprise-grade virtualization at no cost, with optional paid support.
Granular VM and Container Control
Proxmox offers advanced virtualization features such as resource limits, live migration, clustering, and fine-tuned performance settings.
High-Performance Storage
QNAP’s RAID configurations, SSD caching, and optional ZFS support deliver fast and reliable storage performance, ideal for hosting virtual machines or backup data.

Conclusion
storage. Whether you’re backing up VMs to a QNAP NAS or running complex lab environments, this integration allows you to harness the strengths of both platforms, resulting in better control, reliability, and cost-efficiency.
By understanding the best practices and limitations, you can build a setup tailored to your performance, backup, and virtualization needs, making Proxmox and QNAP an excellent choice for modern IT infrastructure.